The V164-8.0MW is now offered with a power mode of up to 8.4MW. This software-based functionality is possible under certain operational conditions, but must fit into the IEC designs specifications envelope. The 0.4MW represents a 5% increase of the certified rating that is allowed within the IEC type certificate.
Minor modifications
Upgrading to 9.5MW involved reapplying the electrical, mechanical, structural and thermal design reserves without sacrificing on design safety factors. The modifications are generally minor, requiring no changes in the main dimensions.
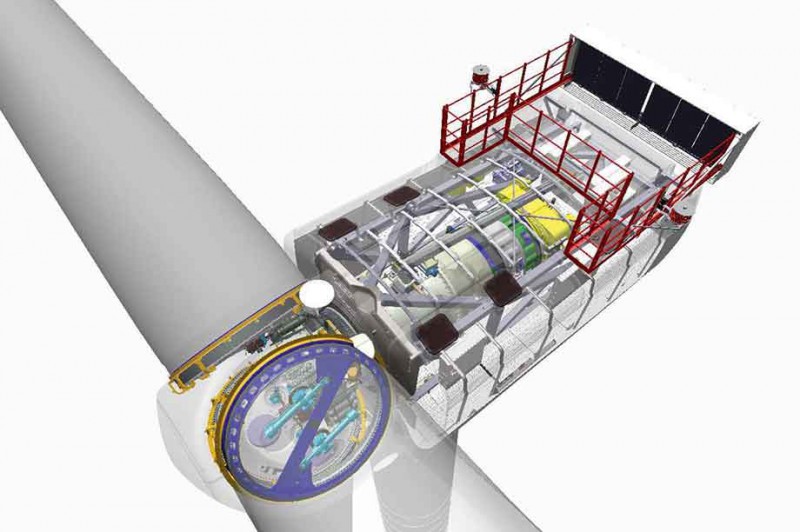
Beneath the surface… Dimensions will stay the same, with changes confined to the inside of the turbine
"Rated gearbox input torque has increased by 19% to 9.5MNm and required some gearbox strengthening without impacting the outer drivetrain and mass," said Andersen. That still leaves it a little short of the Adwen 8MW gearbox’s rated input torque of 9.9MNm.
"We also upgraded the electrical system and functionally modified the rooftop cooler for the gearbox, generator, hydraulics and rectifier, but without having to enlarge the total cooler size and operational aspects.
Business case
The upgrade reflects the dramatic changes seen in the offshore wind environment over the past few years. "In 2009, when V164 product development started, offshore Capex was high due to smaller turbines, a limited track record, offshore substation inclusion, a high-risk profile and a high cost of capital," said Andersen.
"But today, offshore substations and export systems have largely been taken out of wind project Capex, average turbine size has more than doubled, and the cost of capital and risk profile has also reduced a lot, and is likely to come down further."
Andersen illustrated the benefits of power uprating over rotor enlargement with a comparison of alternative scaling options and their effect on LCOE. An 855MW project could have either 106 8.1MW turbines with an enlarged rotor, or 90 of the 9.5MW unit.
A bigger rotor would boost annual energy production (AEP), but that raises turbines loads and requires an increase in hub height to maintain minimum wave clearance.
 手机浏览网
手机浏览网








